General Overview - Quick Guide
Apr 8, 2022

What is OSC See?
OSC See is a timeline-based editor for OSC protocol commands. It enables you to connect with any software that supports the OSC protocol. To establish the connection, you need to assign the input and output ports and define the IP address, whether it's remote or localhost.
With OSC See, you can create Tracks, which act as timelines, allowing you to Record, Edit, and Live-record OSC protocol commands. You can record commands by receiving them from your favorite software in Record Mode or by directly creating them in the track's editing window.
The core dynamic of OSC See - Tracks!
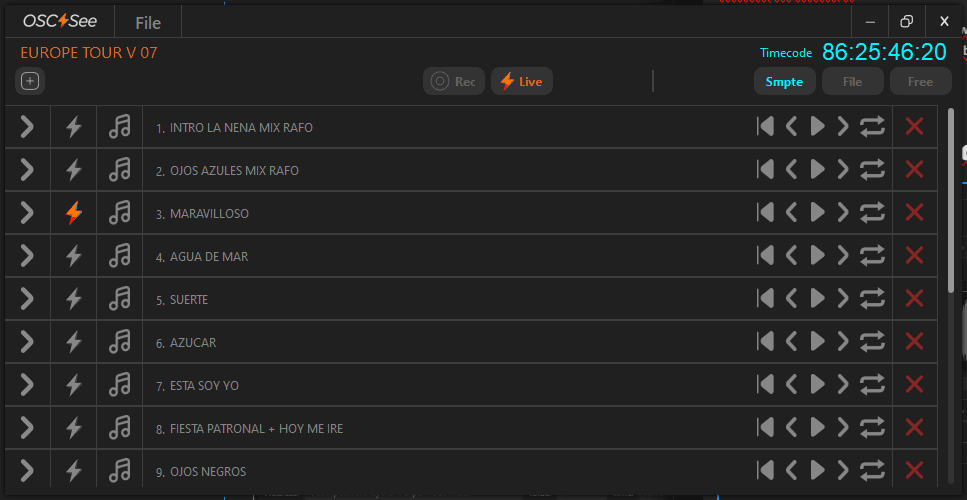
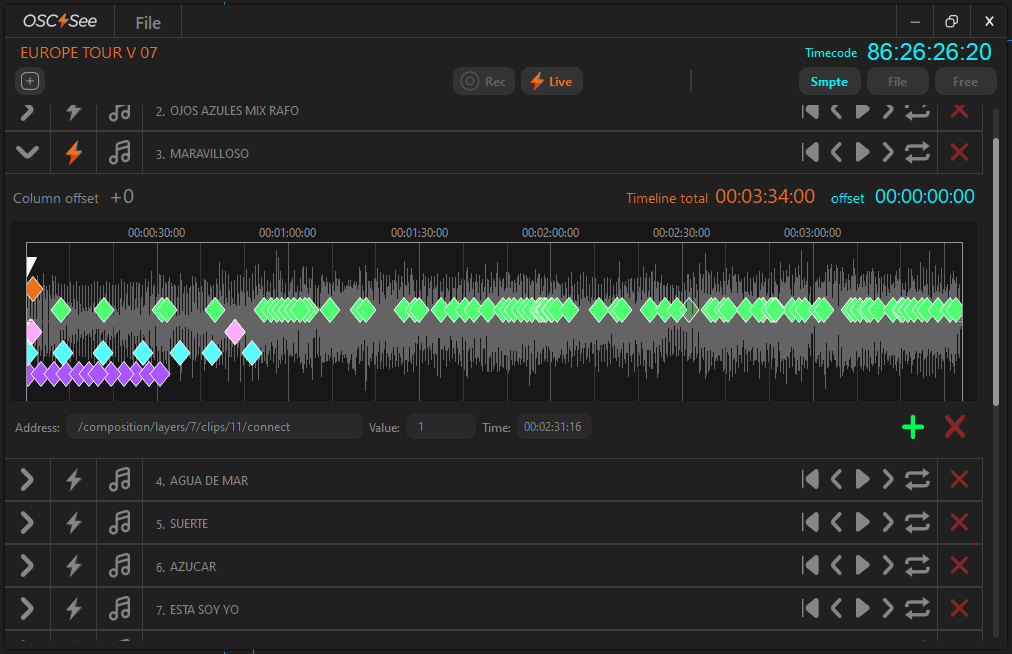
Tracks are the main core of OSC See, each track basically is a timeline where you can create keyframes or commands to control your favorite OSC Software.
NOTE: You can customize the track name by editing the text directly on the track. Additionally, you have the flexibility to rearrange the track order by simply dragging them to a different position.
You may create or add a track just using the + sign on the top left corner.
Track Timecode
These tracks can be controlled or executed by three different Timecodes:
SMPTE LTC - Linear Timecode (SMPTE Protocol) provided by an external audio input. To receive the SMPTE signal, you need to configure the audio input in the Settings Window first.
File - In "File" mode, you can load any audio file onto tracks. To listen to the track, ensure correct audio output configuration in the settings window.
Free - A timeline is created that runs independently, without synchronization to any external source.
SMPTE LTC Timecode:
SMPTE LTC (Linear Timecode), also known as SMPTE timecode, is an industry-standard synchronization protocol developed by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) for precise time synchronization in film production. LTC is a specific format of SMPTE timecode that encodes time information in an audio signal. It represents hours, minutes, seconds, and frames and is typically recorded on audio tracks of video or audio tapes, ensuring precise synchronization during post-production and playback.
SMPTE LTC is widely used in the film and television industry due to its reliability and compatibility with various equipment. It offers frame-accurate synchronization, crucial for editing, dubbing, visual effects, and audio post-production. Despite its age, it remains in use alongside newer synchronization technologies.
The protocol has evolved to support different frame rates and formats for various video standards, providing highly precise and consistent time references. SMPTE LTC continues to be a fundamental and recognized standard in the entertainment industry, thanks to its proven reliability in maintaining synchronization in media production workflows.
In each track you can change the Timecode control between the 3 sources, SMPTE, File or Free, you may create your track Commands on File Mode and then Switch to SMPTE Mode to execute the Timeline and Commands on the correct and exact time.
LTC SMPTE Timecode Offset feature
You can do offset, when you added a track, just adjust the offset time per track, only click on any part of the time, and the offset will be adjusted.
File source - Timecode:
In OSC See, the "File" mode offers a versatile feature that enables users to import audio files onto tracks, providing enhanced control and creative possibilities. This mode conveniently allows you to incorporate pre-recorded audio content into your timeline-based projects.
When you select the "File" mode, you gain the ability to import audio files in various formats (e.g., WAV or MP3) directly into OSC See. This feature is complemented by the Waveform visualization, one of OSC See's core functionalities. This combination unlocks a wealth of opportunities for synchronizing your visuals and effects with specific audio segments, ultimately leading to the creation of captivating and immersive experiences.
Note: on Mac OS X, Waveform visualization is only available for WAV files only.
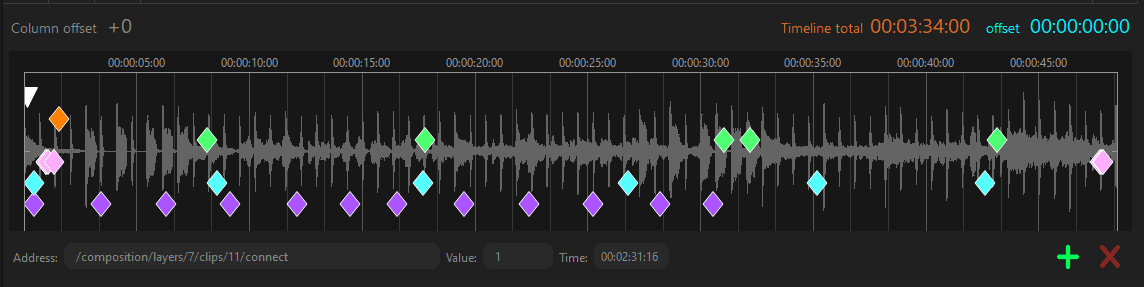
Free source - Timecode:
In OSC See, the "Free" mode offers a powerful and flexible feature that allows you to create a timeline that operates independently, without the need for synchronization to any external source. This mode provides you with complete freedom and control over the timing and execution of your commands and sequences.
When you enter the "Free" mode, you have the ability to define a timeline within OSC See that is not bound to any external time reference. This means that the timeline runs autonomously, following its own internal clock. You have full control over the duration and sequence of events within this timeline.
In the "Free" timeline mode, you have complete freedom to create and manipulate OSC protocol commands without being limited by external timing constraints. This unrestricted approach allows for experimentation and precise customization of sequences to achieve your desired artistic or technical results.
This mode offers the flexibility to add, edit, or remove commands at any point in the timeline, enabling the creation of dynamic and intricate compositions. It also facilitates real-time adjustments during performances or installations.
The "Free" mode in OSC See is versatile, catering to both artistic and corporate applications. It grants you total creative control, making it possible to generate sequences independently of external timecode or audio inputs. This unleashes your creative potential, allowing you to design unique audiovisual experiences tailored to corporate events. You can choreograph visuals, effects, and lighting cues with precision, ensuring a seamless flow and the ability to adapt on the spot.
OSC See Communication Modes:
A. Neutral Mode:
The program doesn't record or play OSC commands. This mode is when you do not push any mode, Record or Live
B. Record (Rec) Mode:
The program records any received OSC commands from other programs. (Note: To record commands, you need to activate the desired command types and their sources in the "OSC Addresses" window in OSC See). Obviously you need to push the REC Button on the Main Window.
C. Live Mode:

In Live Mode, OSC See emits the recorded OSC commands to different IPs or programs. It's important to note that OSC See emits commands from one track at a time to ensure precise show control and avoid accidental activation of sequences from incorrect tracks (which can occur when using the same timecode with LTC SMPTE in a setlist).
Super important note:
To activate communication per track in Live Mode, click the Live button in the control bar and enable the Lightning Bolt icon for each track to go live!"
This feature is a must, because if not, may run commands from another track in SMPTE mode with the same timecode for example.
Navigation
Pan or scroll across the Timeline
Just use the Spacebar + left click to scroll across the timeline, or press the wheel on the mouse.
Zoom in, Zoom out
To zoom in rotate the wheel or right click the mouse and move around.